Explore H01: One cubic millimeter of the human cerebral cortex
The H01 dataset includes a wealth of data, over 50,000 cells and 130 million synaptic connections. The 3D world of the brain is browsable in Neuroglancer, all included, from large neurons down to single synapses. Below is an overview of some of the cell types and structures available. Click on the links and explore examples in Neuroglancer.
Cell types
Neurons
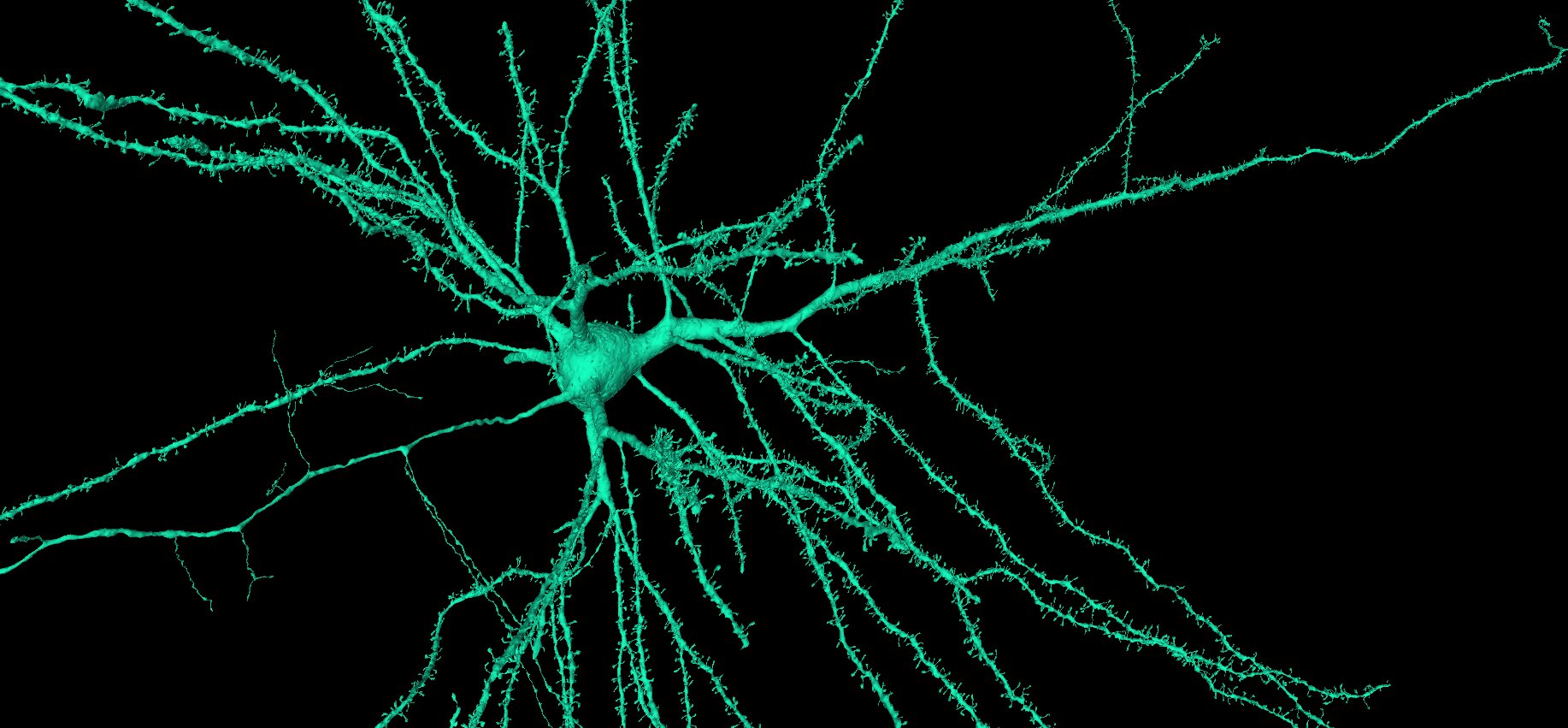
- Pyramidal neurons See just a few examples, see several examples
Pyramidal neurons are the main excitatory neuron in the cerebral cortex, you can find them in all layers except L1, they have a characteristic look and vary in their projections and for example how spiny the dendrites are.
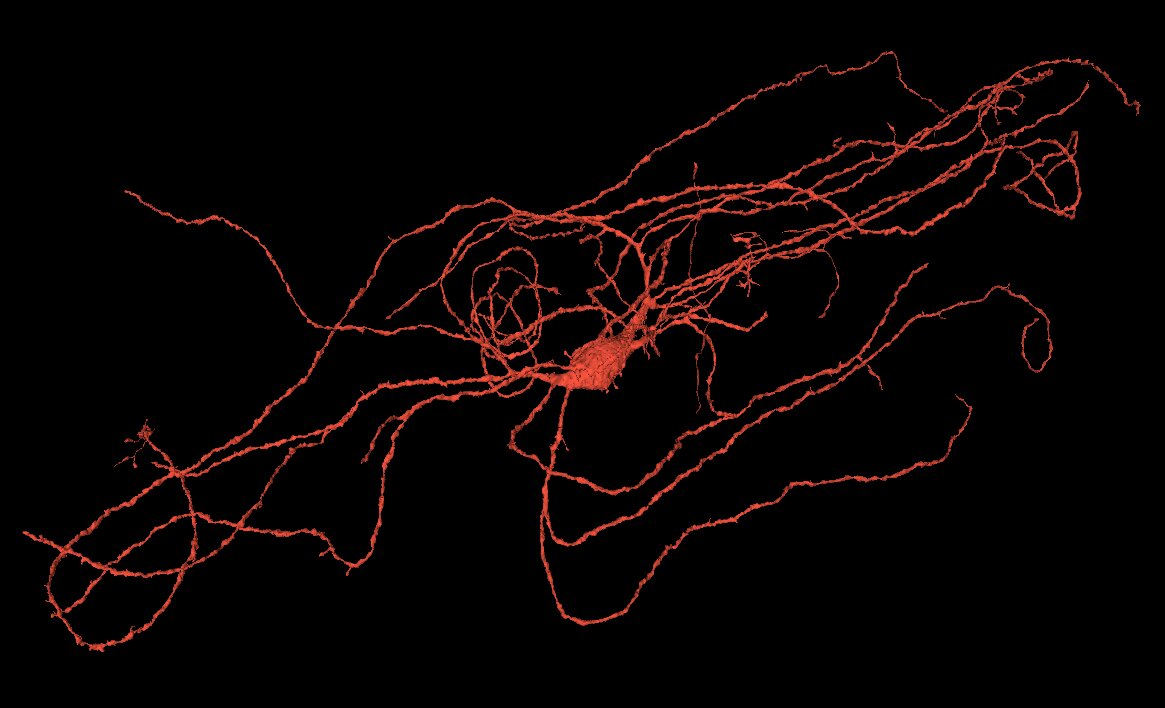
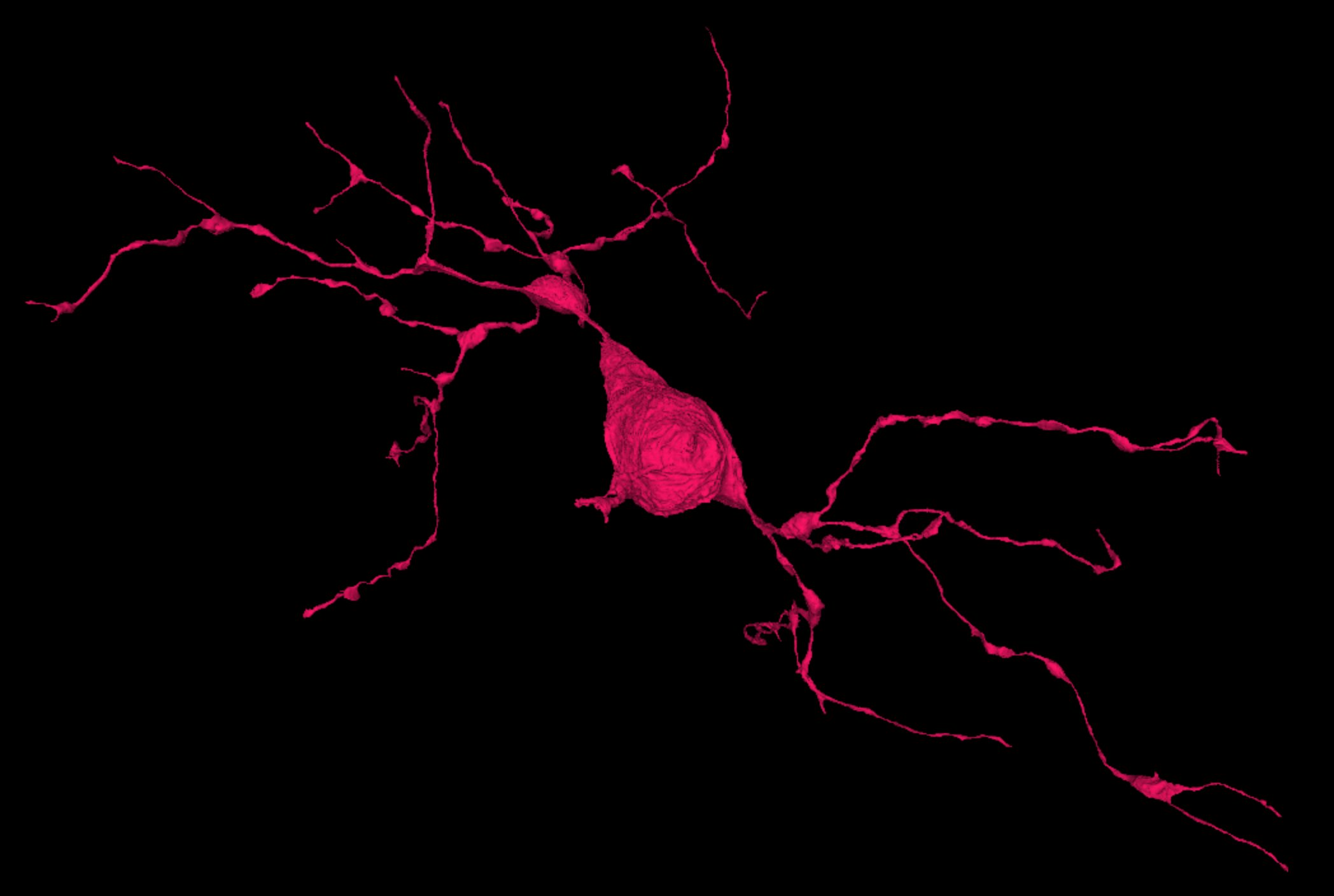
- Interneurons See examples
Interneurons come in different shapes and sizes across the cerebral cortex, they are mainly inhibitory and vary a lot in the number of synapses.
Glial cells
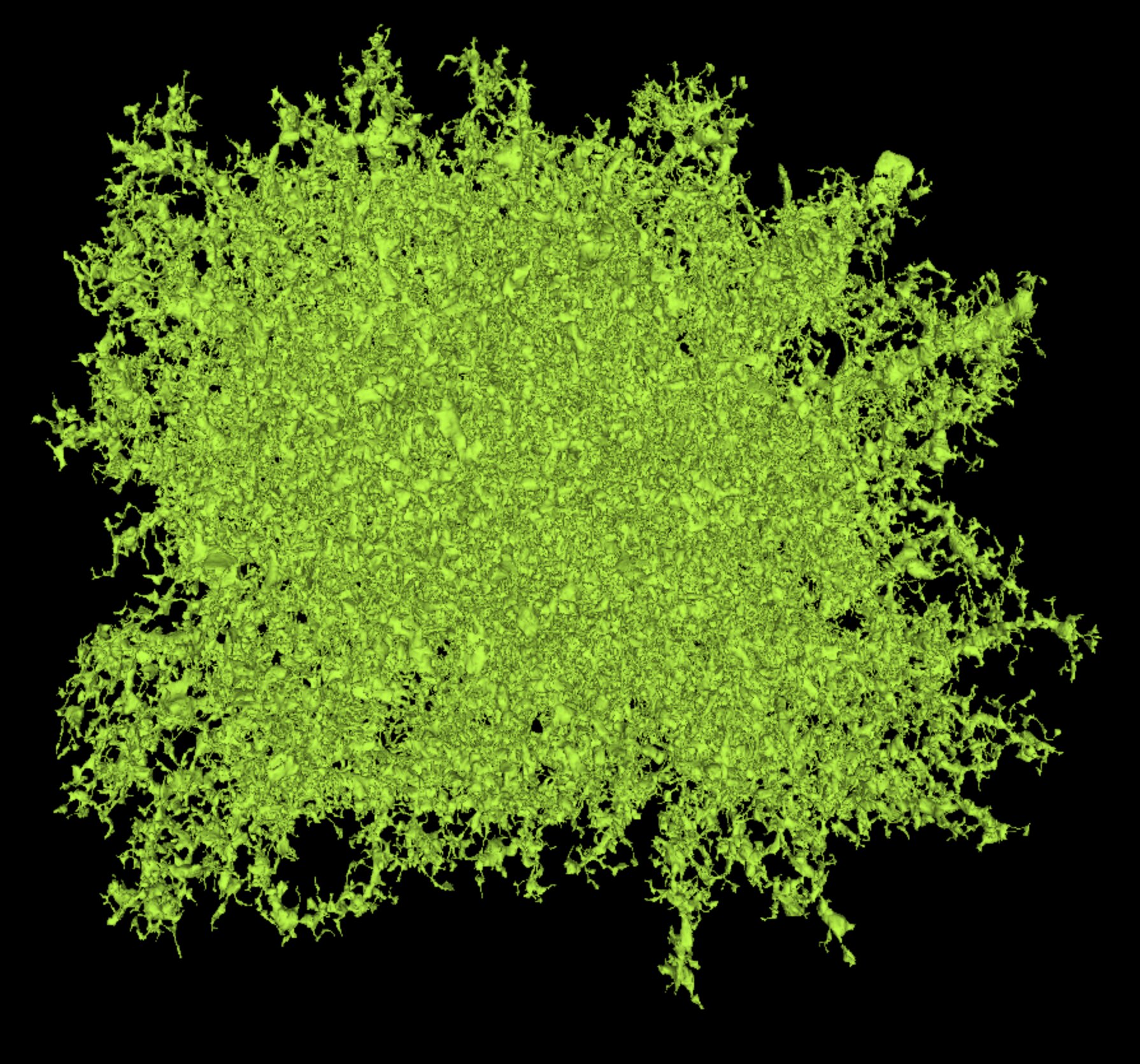
Astrocytes perform numerous functions, some of their main functions are supporting the neurons with energy and neurotransmitter recycle, their endfeet are surrounding the blood vasculature as part of the blood brain barrier.
- Oligodendrocytes See a few examples
Oligodendrocytes main function is myelination of neuronal axons, insulating for faster transmission, potentially also involved in providing axons with energy. Most oligodendrocytes are found in the myelin dense white matter.
- OPC’s and microglia See examples of OPC’s, see examples of Microglia
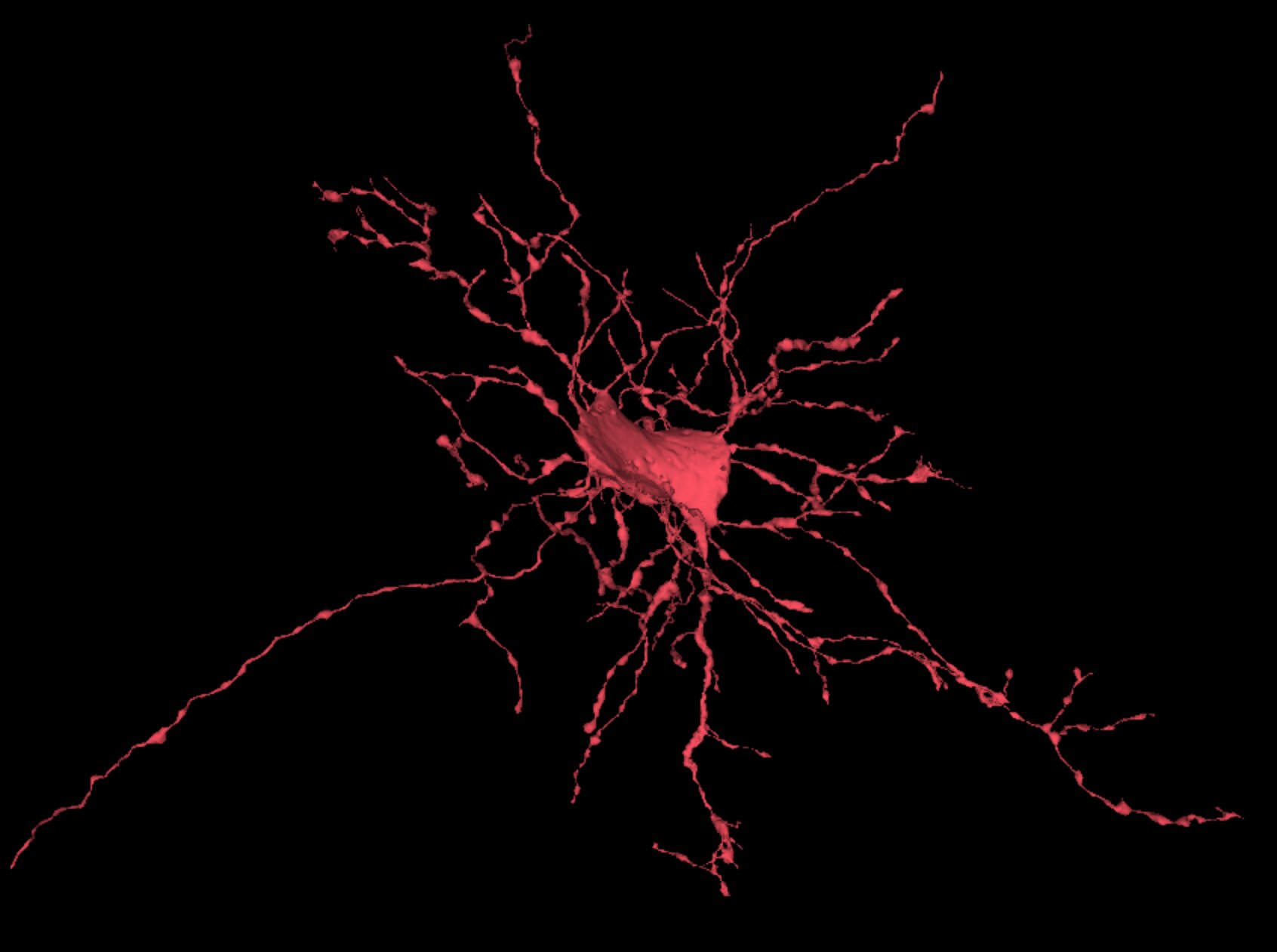
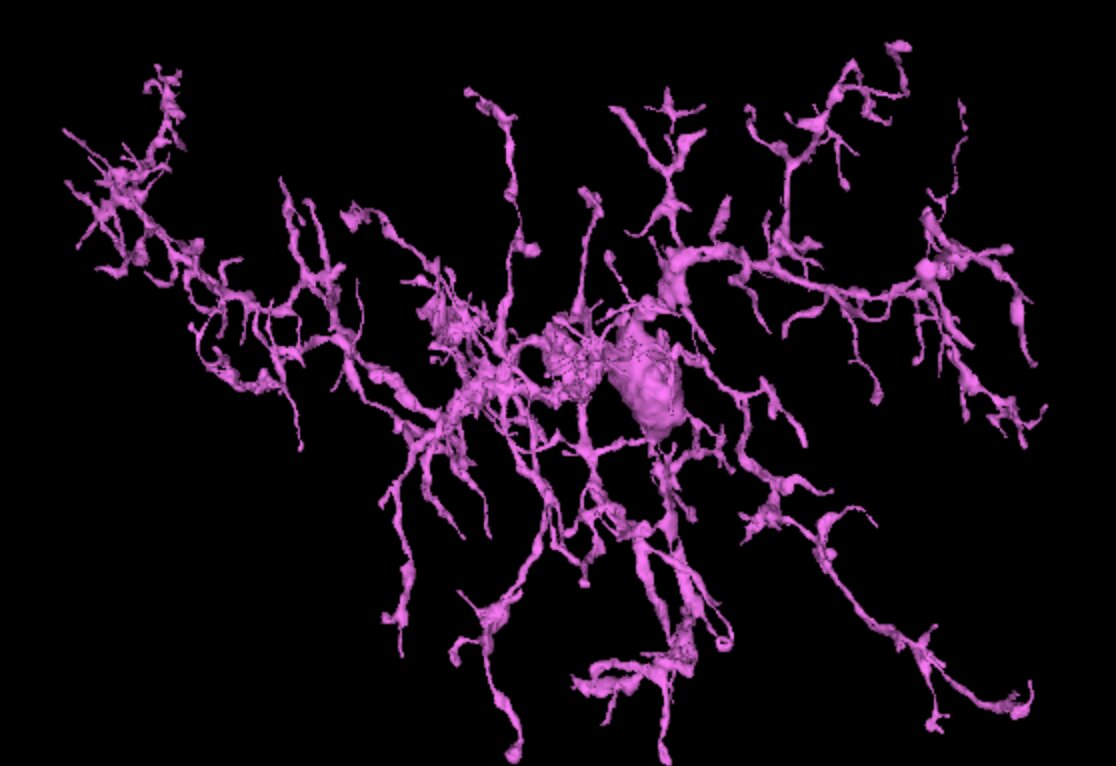
Oligodendrocyte precursor cells (OPC’ s, also called NG2 cells)) are a versatile group of cells that differentiate into oligodendrocytes. Microglia are the local macrophages of the brain, involved in maintaining a healthy brain. OPC’s and microglia share morphological details and are therefore combined in the dataset.
Other details
In addition to the segmented cells that enable a 3D view in the Neuroglancer tool, several details of the brain are available for further investigation using layers.
- Myelin
The characteristic insulation of neuronal axons can be displayed in a separate layer.
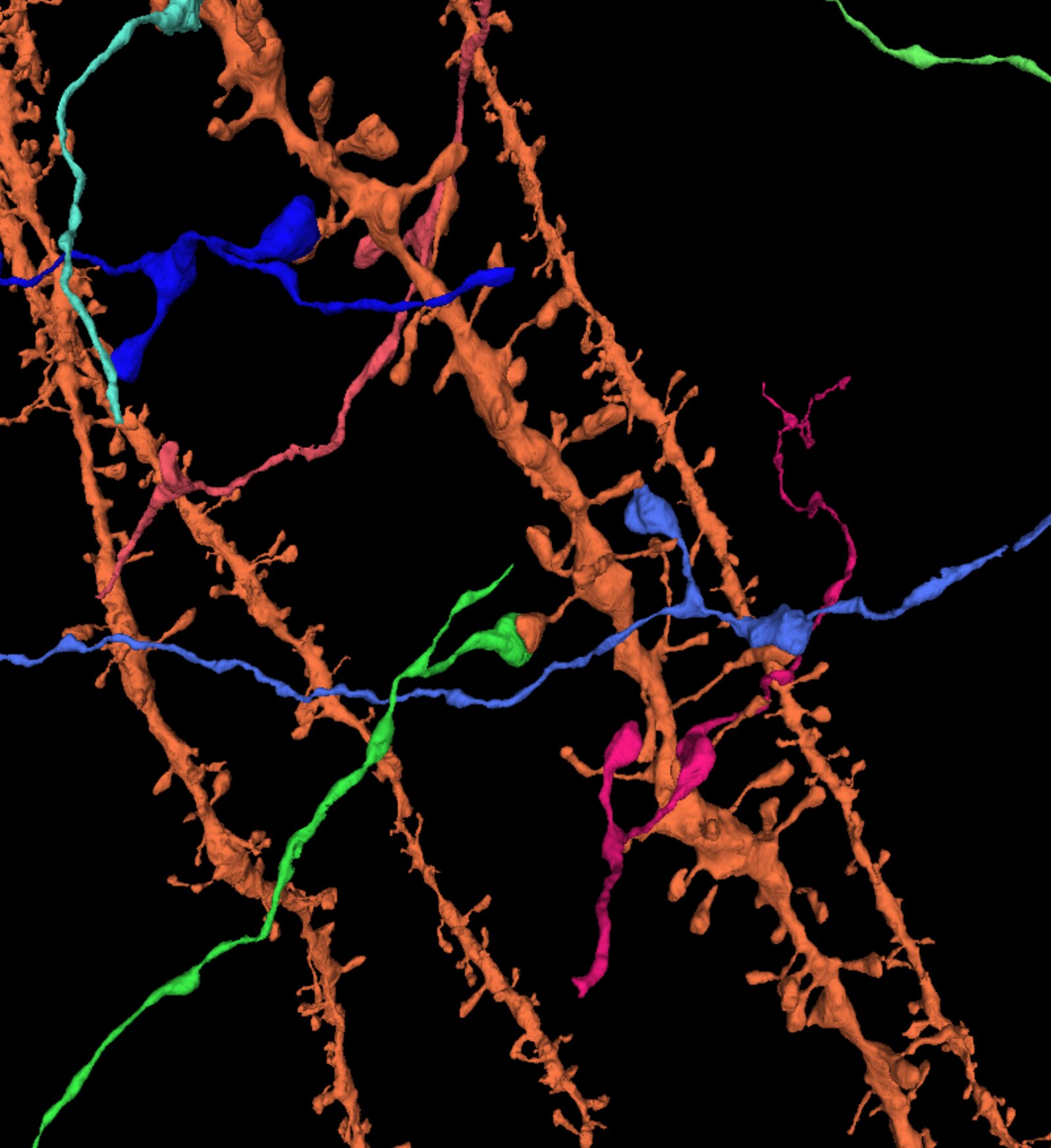
- Synapses See example
All the 130 million synapses are automatically segmented and are highlighted by a separate layer showing each of the pre- and postsynaptic locations in separate colors. Synapses can be separated into excitatory and inhibitory, based on the symmetric or asymmetric pre and postsynaptic sizes.
The 6 layers and white matter of cerebral cortex are shown in a separate layer-function, enable this layer and you can see where your favorite cells are located. The different layers can also be used in combination with cell types in the Neuroglancer search function of segmented cells: simply add L#/WM and the cell type to the query; see for example the “L4 interneurons” as shown in the Gallery.
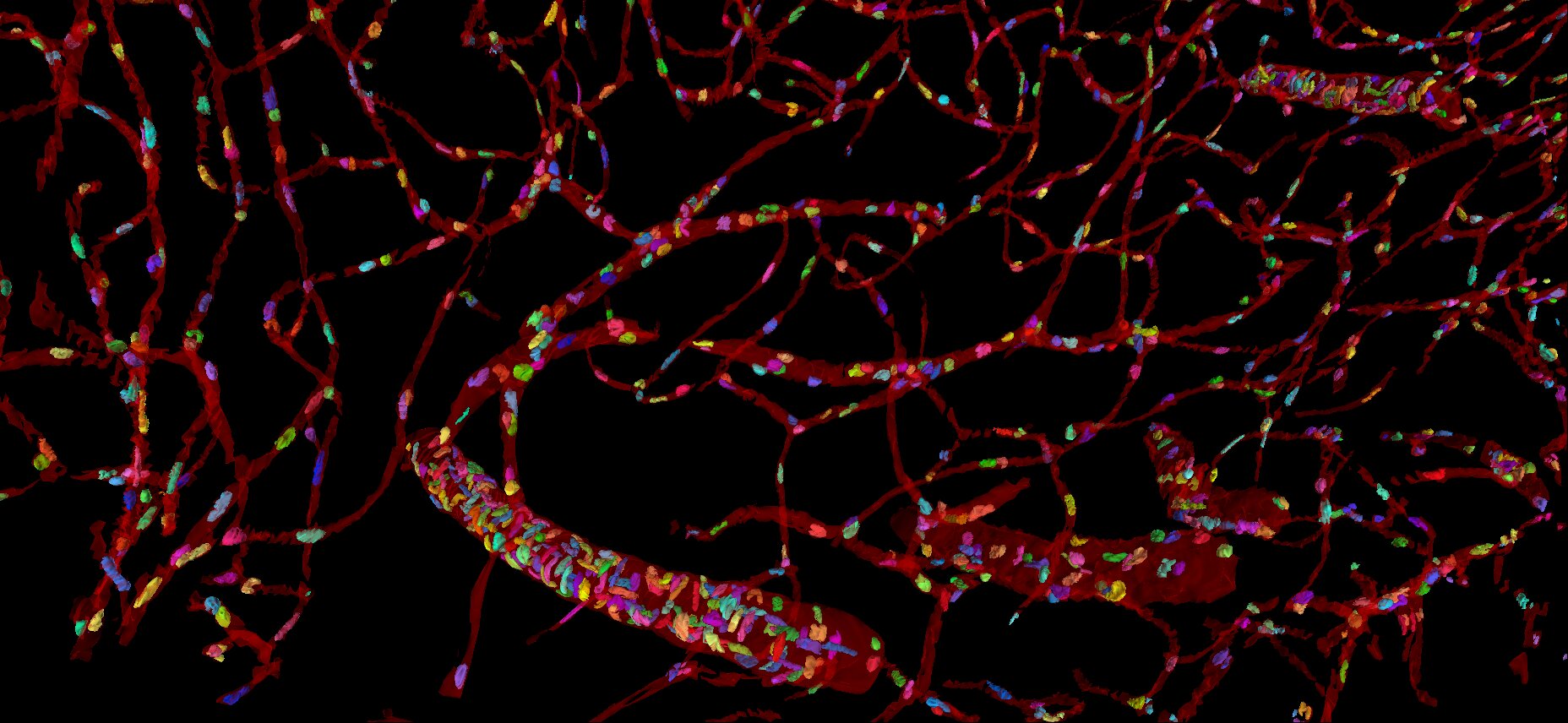
Vasculature
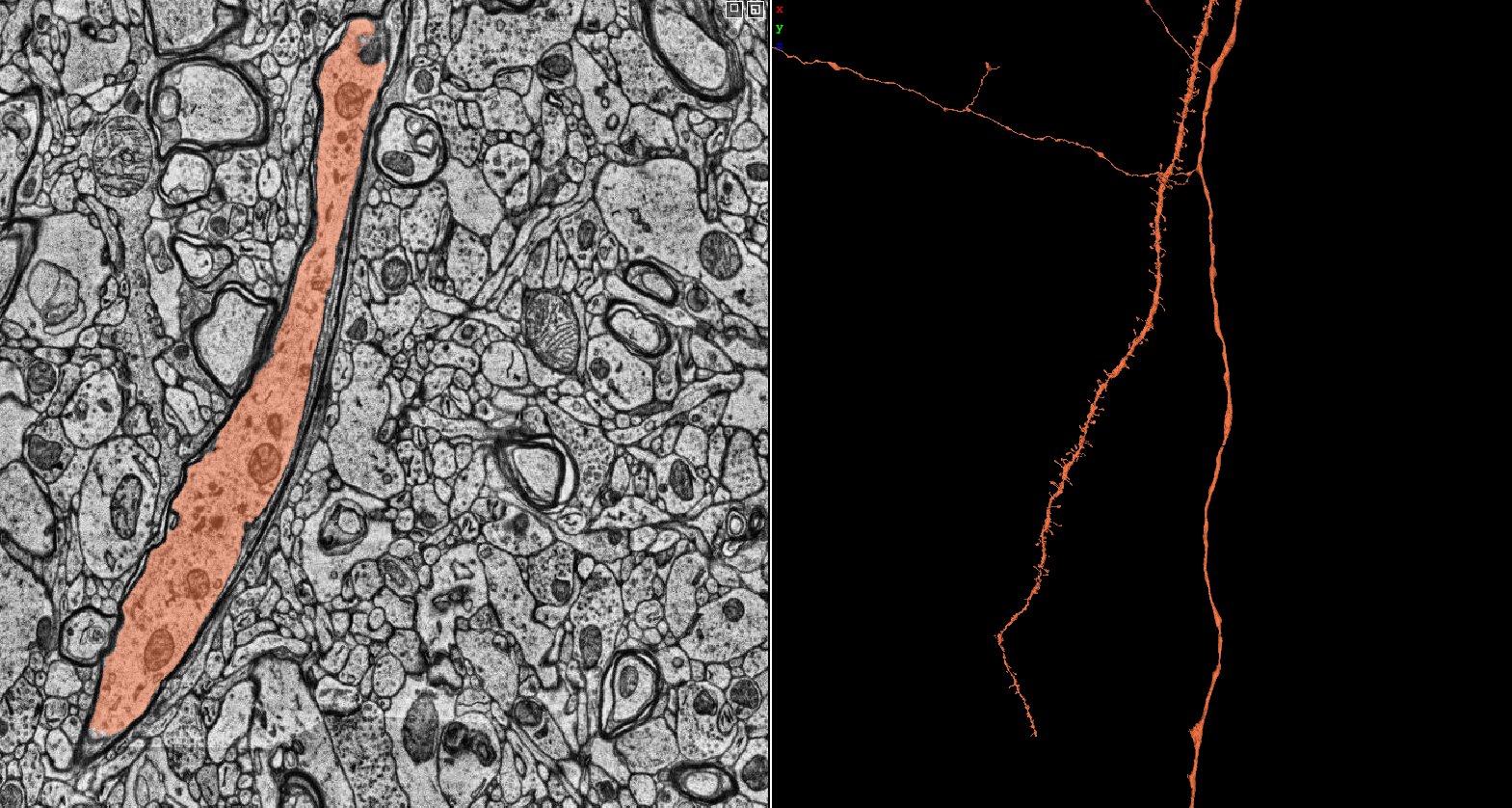
The brain lacks energy storage and therefore requires an advanced vascular system, providing all cells with energy and oxygen. The vasculature and the cells in blood vessels were manually segmented at a low-resolution level.
The vascular system of the H01 brain sample includes different types of blood vessels, including arteries/arterioles and veins/venules, however, the narrowness of the volume limits the possibility to track the blood flow.
- Cell types
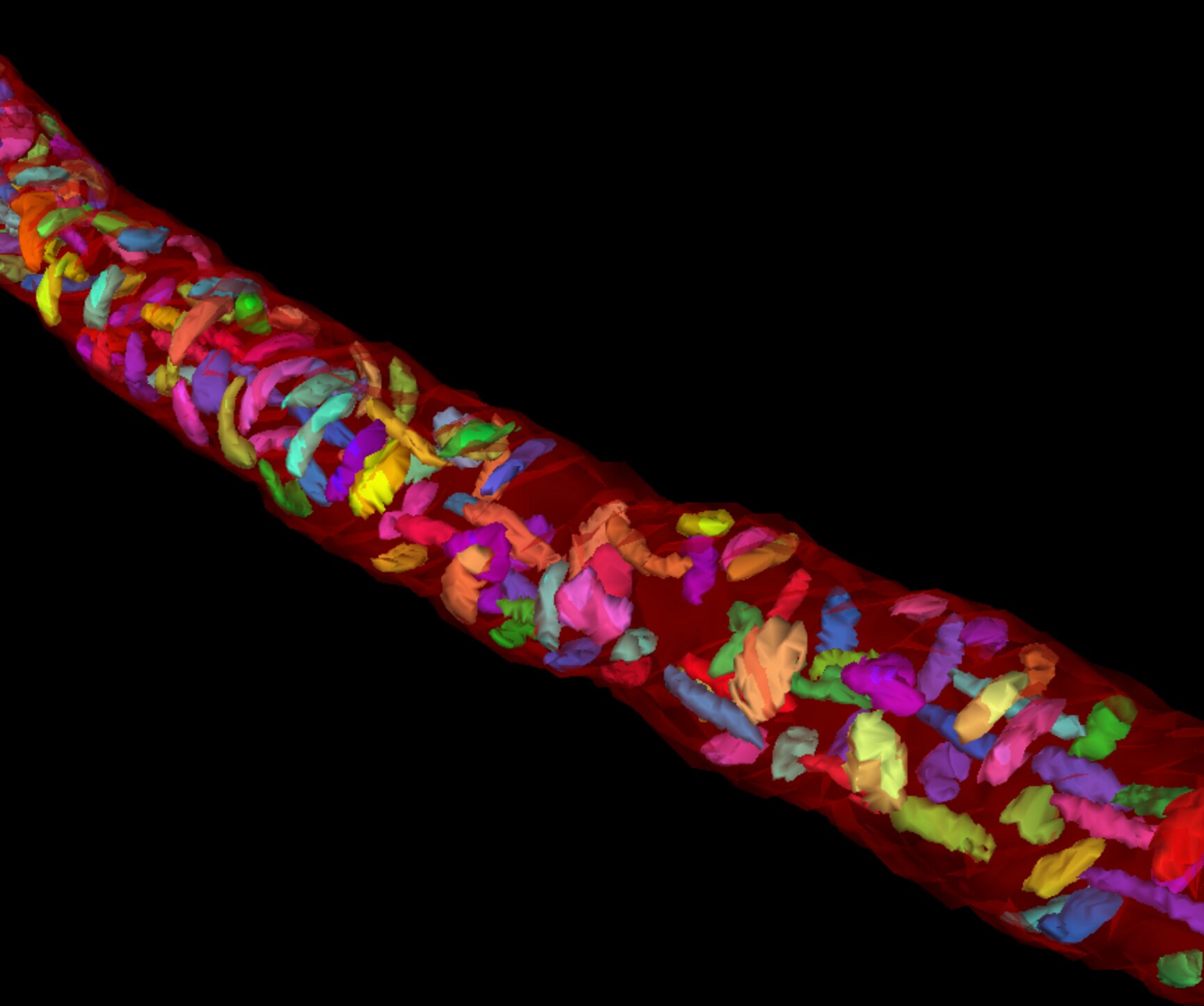
The brain has an important blood brain barrier, restricting the access to the brain. The blood brain barrier protects the brain, while the neurovascular unit controls the blood flow. Endothelial cells and pericytes are important both for the barrier and blood flow. Endothelial cells line the blood vessel lumen, supported by basement membrane and surrounded by pericytes, in larger blood vessels smooth muscle cells. This example shows the cells in an artery, compared to thin capillaries with sparse cells.